In the modern world, electricity powers everything from household appliances to industrial machines, enabling technological advancement across various sectors. At the core of these electrical systems are key components that ensure smooth operation, efficiency, and reliability. Electrical core components, which include a wide range of devices and materials, form the backbone of any electrical system. These components are essential in transforming, controlling, and distributing electrical energy in both simple and complex applications.
Electrical core components are the fundamental parts that make up electrical circuits and systems. These components are responsible for conducting, controlling, storing, and converting electrical energy. They are typically found in virtually all types of electrical devices, from household electronics and industrial machinery to automotive systems and large-scale power grids.
Electrical core components can be broadly classified into passive, active, and electromechanical components, each playing a distinct role in the overall functioning of electrical systems.
Resistors are passive components used to limit the current flowing through a circuit. They play a critical role in controlling the flow of electricity, ensuring that electrical components receive the proper amount of power. In most electrical devices, resistors are crucial for stabilizing voltages, protecting components from damage, and balancing circuits.
Capacitors are essential for storing electrical energy and releasing it when needed. They are used for filtering, smoothing, and stabilizing voltage levels in power supplies. Capacitors also have applications in energy storage, noise reduction, and frequency modulation, making them vital in signal processing, power systems, and telecommunications.
Inductors, like capacitors, are passive components, but they store energy in a magnetic field rather than in an electric field. They are widely used in power supply circuits, signal filtering, and energy storage applications. Inductors are essential in electrical transformers and in high-frequency applications, such as radio transmitters and receivers.
Transistors are active components that act as switches or amplifiers in electrical circuits. They are integral to controlling the flow of current in modern electrical devices, from computers to mobile phones. By amplifying or switching electrical signals, transistors form the core of integrated circuits, which are used in virtually every electronic device.
Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in only one direction. They are primarily used for rectifying alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) in power supplies. Diodes also serve in signal modulation, protection circuits, and in controlling the flow of electrical power in various systems.
Fuses and circuit breakers are protective devices that prevent electrical circuits from overloading. They are designed to interrupt the flow of electricity in the event of a short circuit or when the current exceeds a safe limit. These components are crucial for preventing damage to electrical equipment, fires, and other hazards associated with electrical faults.
Transformers are electromagnetic devices that transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through inductively coupled conductors. Transformers are essential for stepping up or stepping down voltage levels in power distribution systems, ensuring that electrical energy is delivered efficiently to homes, businesses, and industries.
Connectors and switches are essential for establishing or interrupting the flow of electricity in electrical systems. Connectors link electrical circuits and devices, while switches control the on/off status of these devices. These components are integral to the operation of electrical systems, ensuring that they can be safely managed and controlled.
Relays and contactors are electromagnetic switches used for controlling electrical circuits. They are widely used in industrial control systems and automation, where they help to control high-power circuits with low-power signals. These components are vital for safely controlling large machines, motor systems, and industrial equipment.
Electrical core components are designed to work seamlessly together to ensure that electrical systems are reliable. A failure in any one of these components can lead to system malfunctions, equipment damage, or safety hazards. Proper selection, integration, and maintenance of these components are critical for the overall reliability of any electrical system.
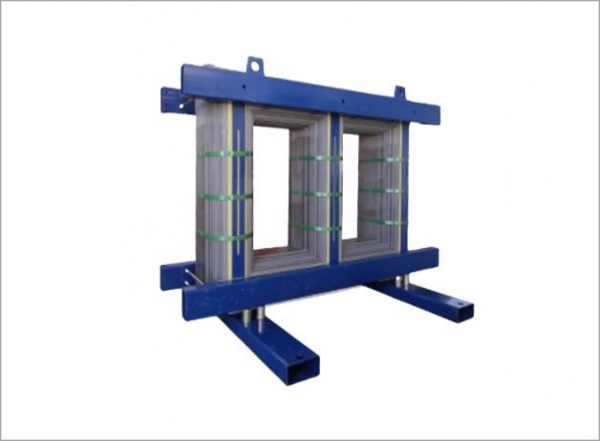

Efficient electrical components minimize energy loss and ensure that electrical systems operate at peak performance. For example, capacitors and inductors are often used in circuits to optimize power quality by filtering out noise and maintaining voltage stability. Similarly, transformers help optimize the voltage levels for efficient power distribution.
Efficient electrical core components help reduce long-term operating costs. By ensuring that electrical systems function correctly, these components prevent breakdowns and the need for expensive repairs or replacements. For example, properly sized resistors and capacitors can help improve energy efficiency, reducing power consumption and operating costs in the long run.
One of the most important roles of electrical core components is ensuring safety in electrical systems. Fuses, circuit breakers, and surge protectors are key to safeguarding electrical systems against overcurrent, short circuits, and electrical surges, all of which could otherwise lead to fires, explosions, or equipment damage.
The advancement of electrical core components directly influences innovation in the electrical and electronics industries. From enabling the development of smaller, more efficient devices to facilitating new technologies like electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, these components play a fundamental role in the continued progress of electrical engineering.
Electrical core components are used across a wide range of industries and applications:
Components like resistors, transistors, and capacitors are crucial in the design of everyday electronics like smartphones, televisions, and computers.
Transformers, circuit breakers, and relays are used in power generation, transmission, and distribution systems to ensure reliable and safe delivery of electricity.
Electrical components in cars, including sensors, relays, and connectors, play a key role in modern automotive technology, especially with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs).
In factories and manufacturing plants, components such as motors, transformers, and contactors are essential for automation and machinery operation.
Components like diodes, capacitors, and inductors are used in telecommunications equipment for signal processing and energy conversion.
 +86-523 8891 8899
+86-523 8891 8899  +86-523 8891 8266
+86-523 8891 8266  info@tl-core.com
info@tl-core.com  No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China
No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China 

 English
English Español
Español Türk
Türk 中文简体
中文简体